Learn How To Spot & Control The Following Pests
Occasional Invaders
We have in our library a variety of insects that could invade your home thru cracks in the foundation and could make your life miserable, so we have the right strategy and treatment for you.

Ants
Economic Importance
Ants may affect us adversely by stinging or biting; invading and contaminating food; nesting in lawns, golf courses, or within premises; stealing seeds from seed beds or feeding on germinating seeds; defoliating or gnawing into plants and plant products; killing young poultry, birds, livestock, or game; simply annoying humans and animals with their presence; and possibly, transmitting certain human diseases after crawling over sputum, feces, carrion, and so forth.
Some carpenter ants can cause serious structural damage to wooden structures. However, only a small number of all the ant species are damaging or medically significant due to their stinging behavior, and require control because of these factors.
Identification of Pest Species
Because of the wide variations in feeding and other habits of different ant species, their successful management often requires exact identification of the species involved. This knowledge allows the professional to gain accurate information.
Major Pest Species
Carpenter Ants
Carpenter ants are among the most conspicuous of ants found in and around homes, being large and typically blackish or very dark-bodied.
Foraging workers have rather large mandibles, which they can bite or give a strong pinch.
Carpenter ants will establish nests in a number of different locations. Outdoor sites include stumps, hollow logs, telephone poles, fence posts, or other similar large pieces of wood. Wood that is moist or partially decayed is preferred by many species, especially in the northeastern United States; however, cracks, crevices, and other cavities may be used to start a nest in sound wood.
Ants may be carried into homes in firewood or enter and establish colonies via other routes. Often ants move into a building solely to feed.
Carpenter ants excavate nest galleries in wood. These galleries somewhat resemble the work of termites but can be distinguished by their entirely clean and almost sandpapered appearance.
They are frequently hollowed in moist or unsound wood, although carpenter ants can burrow in sound wood. Carpenter ants do not use wood for food.


Pharaoh Ants
Pharaoh ants are light yellowish to reddish-brown in color. They are found in localized regions throughout most of the United States and part of southern Canada. They have become a common pest in many areas.
They are an important ant pest in homes, apartments, hotels, grocery stores, restaurants, hospitals, nursing homes, and other facilities throughout much of their range.
Their small size, which enables them to get into almost anything, and their very wide food preferences combine to make pharaoh ants difficult to eliminate from structures in many cases.
Pharaoh ants will feed on such a diverse array of materials that the usage of the term food preferences seems inappropriate. However, substances like syrups, fruit juice, honey, jelly, cakes, pies, greases, dead insects, or meats and blood are frequently fed on.
In hospitals, they will often feed on blood and other bodily fluids, medical waste, or intravenous feeding fluids. Occasionally, when a particularly good food resource is found, especially close to the nest, some queens can be seen traveling to and from the food location.
Typically, however, the queens remain in the nest and are not seen, or importantly, cannot be controlled without the use of an effective bait that the foragers must bring back to the nest and feed to the queens.
Ant Control
The proper procedure for ant control in and around homes or other buildings depend greatly on the species of ant involved, the extent and nature of the infestation, and the location of the nest or nests used by the infesting species.
Bedbugs
Bedbug Control and Bedbug Treatments in All the Five Boroughs of New York and Long Island
Pathway Pest Control is at the forefront of pest management technology with our bedbug treatments. Eliminating bedbugs with safe and effective chemical treatments for residential, commercial, and industrial clients. In addition to bedbug detection services, Pathway Pest Control provides treatments for bedbug control to many types of structures, including:
- Private Residences
- Apartments
- Health Care Facilities
- Hotels
- Dormitories
- Truck Trailers
- Food Plants
- Restaurants
- Effectively treats the entire structure and its contents
- Immediate, dramatic reduction of the bedbug population
- No need to evacuate areas adjacent to treated areas
- Kills all bedbug life stages from eggs to adults

Cryonite
We do provide a green, pesticide-free service. Cryonite converts liquid carbon dioxide into particles of dry ice, freezing and killing pests on contact. It acts fast, it is safe, and it is environmentally friendly. Cryonite for your peace of mind. Call for service pricing and more information (718) 565-5332.

Hotel Pest Control
Keep Out Unwelcome Pests
Protect your hotel’s brand and reputation from bedbugs and other pests that could ruin your guests’ stay with the Pathway Pest Control hotel pest control program.
We have many years of experience working with hotels, which has enabled us to develop best practice standards to offer the most effective pest control program.
Our hotel pest control program can be customized to suit any hotel size from small to large, and offers fully integrated pest management services, from pest prevention to elimination, as well as pest awareness training for front line staff.
Targeted Pest Control for Hotels
Different parts of a hotel face different pest challenges. Pathway Pest Control will develop customized service programs targeted to specific areas of a hotel to keep these areas pest free.
When we develop a service program for your hotel, we will ensure that your business complies with all international and local regulations relating to pest control and health and safety.
Cockroaches

Who doesn’t have a fear of cockroaches? Most homeowners does and they are embarrassing not to mention the range of diseases they carry. Cockroaches also carry a wide of protozoa and other microorganisms inside the bodies, some of which may occasionally be the spread of diseases to humans.
Cockroach Damage and Health Implications
The presence of cockroaches is often detected by their damage or by fecal matter, call frass, they deposit. These clues can aid in diagnosing a cockroaches problem.
Cockroaches contaminate far more food than they eat. Diseases transmitted as a result of these habits include various food poisoning or gastroenteritis. These same habits, along with the smell imparted by any significant level of infestation, are why people are so disgusted and repulsed by the mere presence of cockroaches. Cockroaches' excrement and cast skin also contain a number of allergens to which many people exhibit allergic responses, such as skin rashes, watery eyes, and sneezing. For some very allergic people and particularly for those who also have a chronic lung disease such as asthma, allergic attached to cockroach allergens can be serious and even life-threatening. All forms of contact with cockroaches should be kept to a minimum.
Schedule your free inspection today by calling (718) 565-5332 or book online.
Our Service
The best in pest control, we actually treat for them unlike our competitors, we use the best pesticide available to us and our service is 100% guaranteed.
To protect and prevent call us now and set up your year round protection plan at (718) 565-5332
German Cockroach
In homes, German cockroaches are most commonly found in kitchens, other areas of food storage or consumption, and bathrooms (Shuster and Provonsha).
The German cockroach is the only common house-infesting species that carries the egg capsule for an extended period.
Capsules removed from the female more than a couple of days before the normal hatching time will be less likely to hatch unless they remain under conditions of high humidity.
German cockroaches in a moderately to heavily infested apartment can move into or out of the kitchen area within a week’s time. Adult males appear to be the most mobile stage, followed by nongravid adult females.
Facts: German cockroaches can survive for up to one month without food and two weeks without water.

Fleas
Fleas are pests of humans and their domestic animals all over the world. While most fleas prefer nonhuman hosts, many can and do feed readily on humans when infestations are heavy or when other hosts are not available.
Adult fleas have piercing-sucking mouthparts to penetrate the skin of the host and suck blood. Fleas have a complete metamorphosis.
They are frequently laid on the host animal but may be laid by adults that have fallen to the ground (e.g., into carpeting or the host’s bedding). Since flea eggs are not attached to the host, those laid on the host will fall off and hatch on the ground, in nests or bedding, carpets, upholstery, or cracks in the floor.
A female flea will lay a few eggs each day until she has laid up to 200 to 400 eggs, which will hatch in anywhere from 2 days to a week, but most will hatch within 2 to 3 days under favorable conditions.

Ticks
Tick management to make it more difficult for ticks to get on the body, individuals walking in tick-infested areas should avoid sitting on the ground or on logs in areas with brush and long grass. Repellents containing DEET can be applied directly to the skin while those containing permethrin are generally applied to socks and trouser legs.

Flies
Flies of many kinds have affected humans and human welfare for thousands of years. Some flies suck blood; others are scavengers. Many transmit disease organisms; some are pests of cultivated plants; some live at the expense of other insects; and others aid in the pollination of plants.
Fly Management
For house flies, blow flies, and stable flies, good sanitation is the basic step in all fly management.
Whenever possible, food and materials on which the flies can lay their eggs must be removed, destroyed as a breeding medium, or isolated from the egg-laying adult. Killing adult flies will reduce any infestation.
Elimination of breeding areas is necessary for good management. Where flies are a problem in buildings, the owner or occupants may be able to do this work; the pest management professional’s job is to seek out the breeding places and advise how the work should be done.
Termites
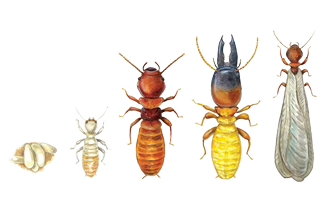
Primary reproductive’s (swarmer termites) are the caste most often seen by homeowners. They have fully developed wings and eyes. The winged adults are usually much darker than the other members of the colony.
All four wings are the same length and extend more than the body beyond the tip of the abdomen. Although functional workers develop in a few months, it usually requires 12 months of progressive colony growth for swarmer termites to occur.
Both male and female reproductive leave the colony in great numbers (swarms), usually in the spring or fall some species swarm in both spring and fall.

These swarms are often the first visible indication that termites are present. Environmental conditions must be just right before termites will swarm. The temperature, moisture (both within and outside the colony), light conditions, and even barometric pressure influence swarming activities.
As a general rule, swarmers emerge on warm, sunny days, when the humidity is high (e,g, often on days following rain showers). After a brief flight, the wings are broken off, and males and females pair and attempt to establish a new colony.
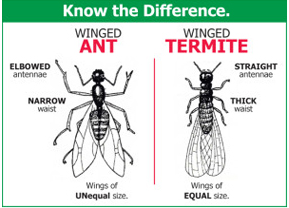
Swarmer termites are often confused with flying or swarmer ants. Since ants are often seen swarming in and around buildings, it is important to distinguish between the two so that appropriate control recommendations ca be made. these are three ways to separate termites from ants. First, ants have a very thin waist between the thorax and the abdomen, while termites are broad waisted. Second, termite wings are all the same size and shape, where as the forewings of the ant are larger, longer, and of a different shape than the hindwings. and the third, termite antennae are straight; ant antennae are elbowed.
Wild Life
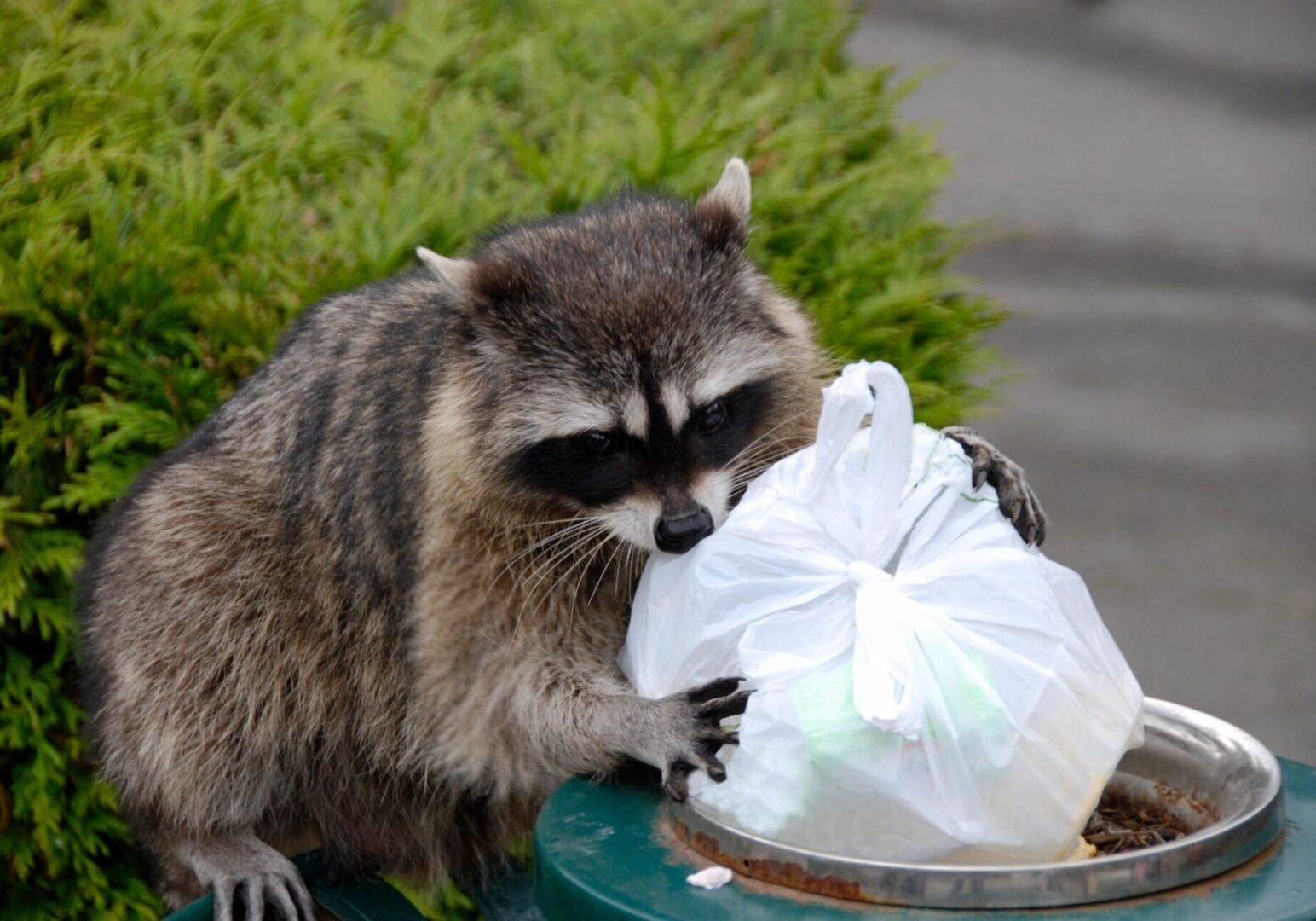

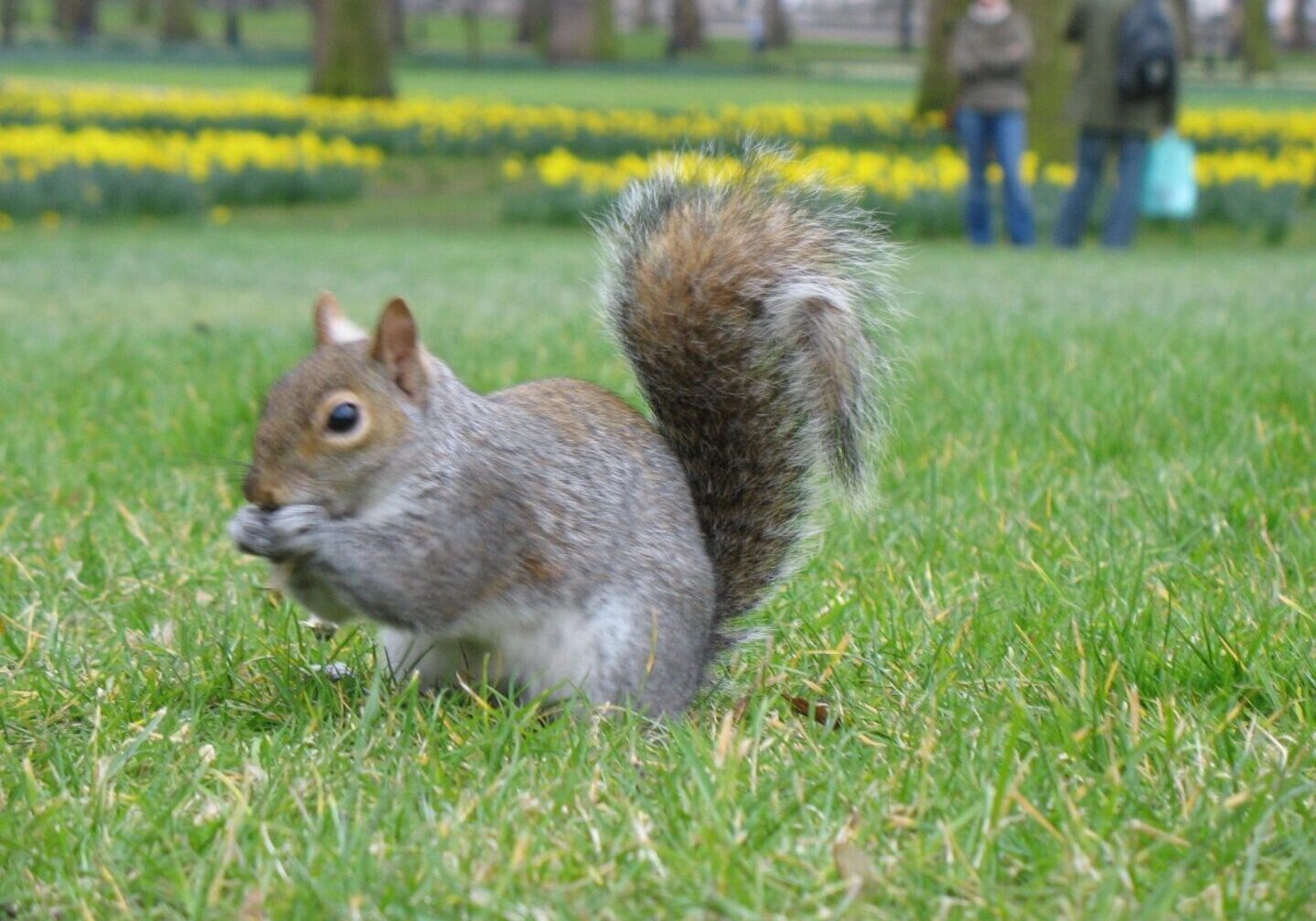
Raccoons and Squirrels
There are four components of urban wildlife IPM programs
• Inspection and analysis
• Sanitation (food and/or harborage removal)
• Exclusion
• Deterring, removing or destroying the offending animal.
Inspection and Analysis
A building or area with wild life problems must be thoroughly inspected to determine the specific areas that are affected. Removing raccoons from a chimney for example requires a much different level of skill and knowledge than live trapping. Next, if possible it should be determined how the animals are gaining entry or access to the structure. This is done via a thorough visual inspection of all foundations, roof and chimney areas for possible structural defects that allow wild life access to the building. The list of factors that may provide long- term control such as sanitation and building repairs should be reviewed with the client at this time.
Sanitation
Wild animals will be drawn to those areas and structures that provide them with their needs for food, water and shelter. For example, garbage must always be placed inside heavy garbage cans with lids secured with shock cord or by a similar means to deny these animals access to the trash.

Exclusion
Nevertheless, most animals are opportunistic in establishing new nest locations, taking advantage of those buildings which allow animal’s easy entry and bi-passing those tightly sealed structures that require excessive effort to gain entry.
Deterring
These approaches can be accomplished via the use of different types of repellents, the use of live traps and where necessary and permitted.
Live Trapping and Removal
Live trapping and removal services are probably the most common type of service performed by wild life damage professionals for infestations of tree squirrels, raccoons, skunks, opossums and woodchucks. Often, in fact, a wild animal needs removal from a building before any other steps can be implemented.
CALL US TODAY FOR YOUR WILD LIFE REMOVAL AT 718-565-5332 OR BOOK ONLINE!
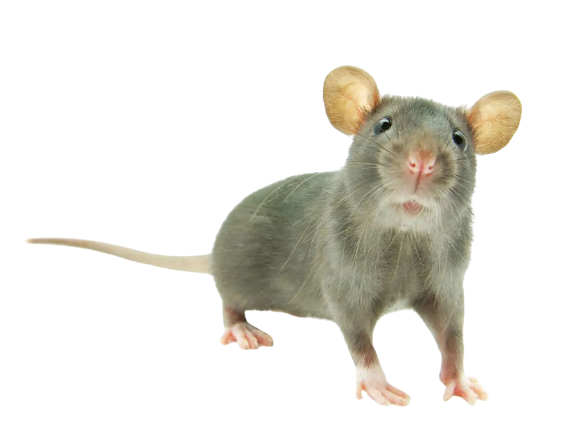
Rodents
Rodents as Health Pests
Rodents have been responsible for, or implicated in, the spread of many diseases to people and domestic animals-especially in years past. Today however because of sanitation, effective drugs, and rodent and insect control programs, the disease threat from rodents is not as significant as it once was.
Mouse allergens
Research in 1999 of children in inner-city areas of eight major cities demonstrated that the house mouse carries a protein within its urine that can trigger severe cases of asthma and allergic rhinitis in susceptible people. Considering that mice typically urinate in microdroplets in many, many spots as they forage about inside a room, literally thousands of micro areas on surfaces can be covered with mouse urine inside homes or schools, offices, etc., that contain significant mouse infestation. As a result of this finding, the ordinary house mouse is considered much more a health pest than in the past.
Salmonella bacteria are actually common in the natural environment. Thus far, it is estimated that about 2,000 different strains (serotypes) of salmonella exist. Certain types are highly pathogenic to people and other animals and can cause salmonellosis (acute food poisoning). Tow serotypes in particular are associated with rodents and food poisoning: Salmonella typhimurius and S.enteriditis.
Salmonella can thrive on decaying food , on poultry and meats, in sewers, livestock facilities, septic tanks, cesspools, accumulated garbage, and other similar unsanitary environments. Because rodents frequent these areas and then visit homes and food facilities, the potential for spread of the salmonella is real because the bacteria thrive in the intestinal tract of rodents, and hence are spread intestinal tract of rodents, and hence are spread through food contaminated with rodent feces.


In the United States, approximately two million cases of salmonellosis occur each year. To date, research has shown that rats and mice may do not play a major role in the direct spread of salmonellosis to humans. In livestock facilities however, such as poultry operations, the house mouse can have significant involvement in amplifying the spread of salmonella.
Rat-bite fever is caused by the bacterium streptobacillis moniliformis that can live in the saliva of both rats and mice. This bacteria causes flu-like symptoms lasting for several days, but in severe cases (which are rare), it can be fatal.
Other diseases the general public (including physicians) sometimes mistakenly associate the bites of rodents with the potential of rabies transmission. But wild commensal rodents have not been found to transmit rabies. Thus, the U.S Public Health Service does recommend specific anti-rabies treatments in the event of rat and mouse bites. Rodents have been implicated with transmitting several other diseases. Lymphocytic chori-omeningitis (LCM) may be spread by mice, as has cities over the past several years. Trichinosis caused by the trichina worn, can be harbored and shed by rats via their feces into hog feed. Rats have also been shown to carry the organisms of typhoid, dysentery, and several other diseases.
Rodents as Economic Pests
Rat and mice attack our food in the farm fields, orchards and livestock facilities, during its processing, storage and transport, and while it is in our supermarkets, restaurant, and homes. In this regards, the rodents have been referred to as pletoparasitic: meaning they parasitize us via staling our valuable resources. They also spoil tons of food by contaminating it with their urine, feces, or fur. The loss of food to rodents worldwide is staggering experts estimate that rats and mice destroy enough food each year to feed 200 million people.
In our buildings, rodents damage doors, floors, ceilings, and walls as a result of their burrowing and gnawing activity. They also regularly gnaw on various utility pipes and electrical wiring resulting in explosions, indoor flooding, fires, equipment malfunctions, and power shortages.
In addition to the direct economic losses (and health-associated costs) rodents are also expensive to control. In the United States alone. conservative annual estimates place the cost of rodent pest management programs to be well over $120 million dollars. Worldwide, the cost rodent control is probably in the billions.

